# init repo notebook
!git clone https://github.com/rramosp/ppdl.git > /dev/null 2> /dev/null
!mv -n ppdl/content/init.py ppdl/content/local . 2> /dev/null
!pip install -r ppdl/content/requirements.txt > /dev/null
Lab 04.03.2: Variational Neural Topic Modeling#
## Ignore this cell
!pip install ppdl==0.1.5 rlxmoocapi==0.1.0 --quiet
import inspect
import nltk, re
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow_probability as tfp
from rlxmoocapi import submit, session
from tensorflow.keras.models import Model
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Input, Layer
from tensorflow.keras.initializers import GlorotNormal
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_20newsgroups
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
from tqdm import tqdm
tfd = tfp.distributions
tfb = tfp.bijectors
tfpl = tfp.layers
nltk.download("popular")
course_id = "ppdl.v1"
endpoint = "https://m5knaekxo6.execute-api.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/dev-v0001/rlxmooc"
lab = "L04.03.01"
Log-in with your username and password:
session.LoginSequence(
endpoint=endpoint,
course_id=course_id,
lab_id=lab,
varname="student"
);
Topic Models#
In this lab, we will use a neural network for variational topic modeling. First, let us introduce a general topic model:
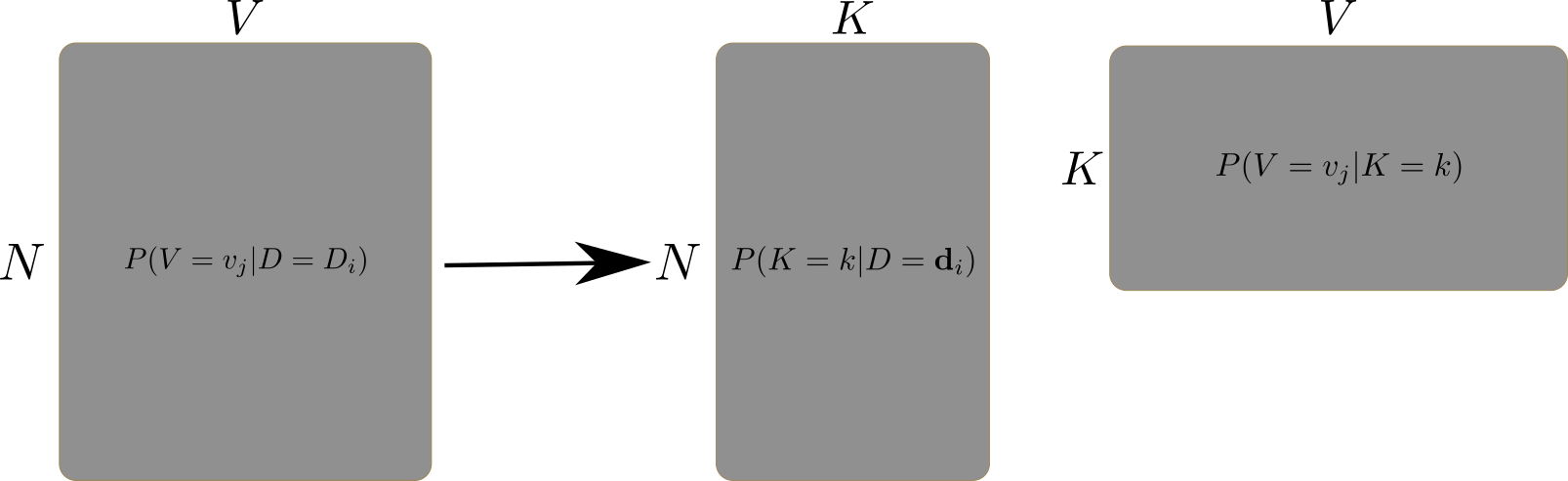
Where:
\(N\) is the number of documents in the corpus.
\(V\) is the vocabulary size.
\(K\) is the number of topics.
\(P(V=v_j|D=d_i)\) is the probability of word \(v_j\) in document \(d_i\) (a Bag-of-Words representation).
\(P(K=k|D=d_i)\) is the probability of topic \(k\) in document \(d_i\).
\(P(V=v_j|K=k)\) is the probability of document \(d_i\) belonging to topic \(k\).
In this case, we will use a probabilistic encoder-decoder neural network to approximate \(P(K=k|D=d_i)\) and \(P(V=v_j|K=k)\).
First, let us load the 20 newsgroups dataset:
newsgroups = fetch_20newsgroups(subset="test")
corpus, labels = newsgroups.data, newsgroups.target
Let us preprocess the data:
def preprocess_doc(doc):
"""
preprocess a document.
"""
lower_doc = doc.lower()
clean_doc = re.sub(r"[^a-z]", " ", lower_doc)
clean_doc = re.sub(r"\s+", " ", clean_doc)
tokens = clean_doc.split(" ")
sw = stopwords.words("english")
filtered_tokens = filter(
lambda token: token not in sw,
tokens
)
return " ".join(filtered_tokens)
preprocessed_corpus = list(map(preprocess_doc, tqdm(corpus)))
print(preprocessed_corpus[:5])
The BoW representation of the documents is a matrix of size \(N \times V\):
bow = (
CountVectorizer(min_df=50)
.fit(preprocessed_corpus)
)
X = (
bow
.transform(preprocessed_corpus)
.toarray()
)
vocab = bow.get_feature_names_out()
print(X.shape)
Task 1:#
Implement the Encoder class that takes the BoW of a document (\(P(V=v_j|D=d_i)\)) as input and outputs a probability distribution over topics (\(P(K=k|D=d_i)\)), you must:
Implement the constructor, adding the
Denselayers that you will need.Implement the
callmethod to connect the input and the layers, and return the output of the last layer.The last layer must be a
Denselayer with aclipped_softplusactivation withn_topicsunits.Use the
GlorotNormalinitializer for the weights.
def build_encoder():
def clipped_softplus(x):
return tf.clip_by_value(tf.nn.softplus(x), .1, 1e3)
class Encoder(Model):
def __init__(
self,
n_topics,
hidden_layers,
activation,
*args, **kwargs
):
super(Encoder, self).__init__(*args, **kwargs)
# YOUR CODE HERE
self.hidden_layers = ...
self.latent_layer = ...
@tf.function
def call(self, inputs):
# YOUR CODE HERE
...
return Encoder
Task 2#
Implement the DecodingLayer, it will receive the latent representation and return the reconstructed input, the layer should implement the following opperation:
Where \(\mathbf{L}\) is the latent representation (output of the encoder) and \(\mathbf{W}\) are the parameters of the layer.
def build_decoder():
class DecodingLayer(Layer):
def __init__(self, n_topics, vocab_size, *args, **kwargs):
super(DecodingLayer, self).__init__(*args, **kwargs)
# YOUR CODE HERE
self.params = ...
@tf.function
def call(self, topics):
# YOUR CODE HERE
...
def get_topic_words(self):
# This function must implement the following operation:
# softmax(W)
...
return DecodingLayer
source_functions = ["build_decoder"]
source_variables = []
res = teacher.run_grader_locally(
"grader2", source_functions,
source_variables, locals()
)
print(res.data)
The prior function creates the prior distribution for the topics, We’ll use this for variational inference.
def prior(n_topics, init_val):
concentration = tf.fill([1, n_topics], init_val)
concentration = tfb.Softplus()(concentration)
return tfd.Dirichlet(concentration=concentration)
prior_dist = prior(n_topics=5, init_val=1.0)
print(prior_dist)
Task 3#
The following class implements the variational neural topic model, you must implement the NeuralTopicModel, such that:
Initialize the
EncoderandDecodingLayerwith the correct hyperparameters, using thebuild_encoderandbuild_decoderfunctions.Initialize a
DistributionLambdalayer for the topics using the dirichlet distribution, and using sampling as theconvert_to_tensor_fnfunction.
The model must implement the following operation:
output = decoder(dirichlet(encoder(input)))
def build_full_model():
class NeuralTopicModel(Model):
def __init__(
self,
prior_dist,
neg_elbo,
n_topics=20,
hidden_layers=(256, 256),
activation="relu",
vocab_size=10000,
*args, **kwargs
):
super(NeuralTopicModel, self).__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.prior_dist = prior_dist
self.neg_elbo = neg_elbo
# YOUR CODE HERE
def call(self, inputs):
# YOUR CODE HERE
encoded = ...
decoded = ...
self.add_loss(self.neg_elbo(inputs, encoded, decoded, self.prior_dist))
return decoded
return NeuralTopicModel
Task 4#
Implement the following loss function:
neg_elbo(X) = mean(log_prob(X) - kl(prior || topics_posterior(X)))
Where:
inputs: is the input BoW.encoded: output of the encoder model, represents the parameters of a Dirichlet distribution for the topics.decodedoutput of the decoder model, represents the parameters of a OneHotCategorical distribution for the reconstructionprioris the prior distribution for the topics.
def neg_elbo(inputs, encoded, decoded, prior_dist):
# YOUR CODE HERE
return ...
source_functions = ["neg_elbo"]
source_variables = []
res = teacher.run_grader_locally(
"grader4", source_functions,
source_variables, locals()
)
print(res.data)
Let us train the model
# hyperparameters
N_TOPICS = 20
HIDDEN_LAYERS = (256, 256)
ACTIVATION = "relu"
prior_dist = prior(n_topics=N_TOPICS, init_val=2.0)
input = tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=(len(vocab),))
neural_topic = build_full_model()(
neg_elbo=neg_elbo,
prior_dist=prior_dist,
n_topics=N_TOPICS,
hidden_layers=HIDDEN_LAYERS,
activation=ACTIVATION,
vocab_size=len(vocab)
)(input)
model = Model(inputs=input, outputs=neural_topic)
model.compile(optimizer="adam")
model.fit(X, epochs=15, batch_size=64)
Finally, let us review the learned distributions.
The posterior distribution of the topics:
topics_posterior = tfd.Dirichlet(model.layers[1].encoder(X))
print(topics_posterior.mean())
print(topics_posterior.stddev())
The probabilities of the words in the topics:
topics_words = model.layers[1].decoder.get_topic_words()
print(topics_words)
Finally, We can view the 15 most relevant terms for each topic:
for i, comp in enumerate(topics_words.numpy()):
terms_comp = zip(vocab, comp)
sorted_terms = sorted(
terms_comp, key= lambda x:x[1],
reverse=True
)[:15]
print("Topic {}: {}".format(
i, " ".join(
map(
lambda x:x[0], sorted_terms
)
)
))

